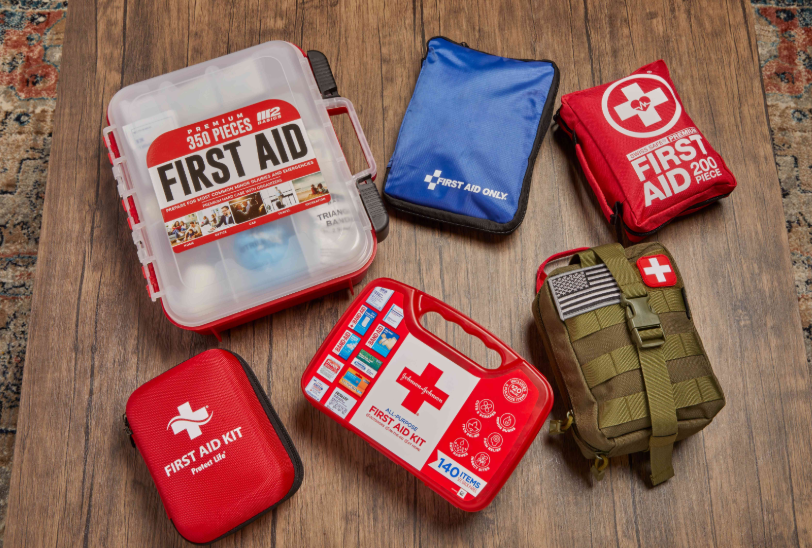
Preserving Lifesaving Supplies in Mobile Medical Kits
Mobile medical kits are vital tools for first responders, home healthcare providers, and disaster relief teams. These portable lifelines can save lives, but their effectiveness relies on the condition of the supplies inside. Proper preservation and storage are essential to ensure patient safety and care.
Risks and Challenges in Mobile Storage
Unlike a stable hospital or clinic environment, mobile medical kits are exposed to a range of challenging conditions that can compromise the integrity of their contents.
Temperature Fluctuations
One of the biggest challenges is maintaining a consistent temperature. Medical supplies are often sensitive to extreme heat and cold. For instance, many medications, including insulin and certain vaccines, must be kept within a narrow temperature range to remain effective. A vehicle left in the sun can quickly exceed safe temperature limits, while cold weather can cause liquids to freeze and vials to crack. This variability requires active temperature management to protect sensitive supplies.
Contamination
Mobile kits are frequently used in uncontrolled environments where exposure to dust, dirt, moisture, and pathogens is a real threat. If sterile supplies like bandages, syringes, or surgical instruments are not sealed and protected, they can become contaminated, posing a significant risk of infection to patients. Cross-contamination between used and unused supplies is also a concern if proper organization isn’t maintained.
Physical Damage
The mobile nature of these kits means they are subject to being dropped, jostled, or compressed. This physical stress can damage fragile items like glass vials, break the seals on sterile packaging, or compromise the calibration of sensitive diagnostic equipment. A disorganized kit where items are not securely packed is particularly vulnerable to this kind of damage.
Best Practices for Organizing and Packing Your Kit
A well-organized mobile medical kit is not only more efficient to use in an emergency but also better protected against damage and contamination.
Use a High-Quality, Durable Bag
Start with a bag or case designed for medical use. Look for options that are made from durable, water-resistant materials and have sturdy zippers or latches. A good medical bag will have multiple compartments, dividers, and elastic loops to keep supplies organized and secure. Hard-shell cases offer the best protection against physical impact.
Group Items Logically
Organize your supplies by category or function. For example, keep all wound care items together, group diagnostic tools in one section, and store medications in another. Some professionals prefer to organize kits based on common medical scenarios, creating smaller “sub-kits” for trauma, cardiac events, or routine check-ups. This approach can save critical time during an emergency.
Label Everything Clearly
Use clear, easy-to-read labels for all compartments and containers. This helps you quickly find what you need without rummaging through the entire kit. It also helps others who may need to use your kit. For medications, include the name, dosage, and expiration date on the label.
Secure All Items
Ensure that all items are packed securely to prevent them from moving around during transport. Use the built-in loops and dividers in your bag. For smaller items, consider using zippered pouches or small plastic containers. This not only prevents damage but also maintains organization.
Preserving Different Types of Medical Supplies
Different supplies have different preservation needs. Following specific guidelines for each type is essential for maintaining their efficacy and safety.
Medications
- Temperature Control: Many medications need to be stored at a controlled room temperature (typically 68-77°F or 20-25°C). For temperature-sensitive drugs like insulin or certain biologics, a medical-grade cooler with cold packs is necessary. Monitor the temperature regularly with a thermometer.
- Light and Moisture Protection: Store medications in their original packaging to protect them from light, which can degrade active ingredients. Use waterproof containers to shield them from moisture.
- Expiration Dates: Regularly check the expiration dates of all medications and rotate your stock, moving older items to the front to be used first. Immediately discard any expired medications according to proper disposal guidelines.
See also: Why ABA Billing Services Are Essential for Patient Satisfaction and Financial Health
Vaccines and Biological Samples
- Cold Chain Management: Vaccines and certain biological samples require strict cold chain management, meaning they must be kept within a specific, low-temperature range from the point of manufacture to administration. This often involves using specialized portable refrigerators or validated coolers with phase-change materials. For certain applications requiring ultra-low temperatures, bulk dry ice might be used for transport, though this requires careful handling and ventilation.
- Monitoring: Continuous temperature monitoring is crucial. Use digital data loggers that can track temperatures over time and alert you if they go outside the acceptable range.
Sterile Supplies
- Inspect Packaging: Before packing, inspect the packaging of all sterile items, such as gloves, bandages, and syringes. Discard any items with torn, punctured, or compromised packaging.
- Protect from Moisture and Compression: Store sterile supplies in a dry, dedicated compartment of your kit. Avoid overpacking the kit, as compression can break the seals on sterile packages.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Healthcare is a highly regulated field, and the storage of medical supplies is no exception. It is essential to be aware of and comply with all relevant regulations from bodies like the FDA, state boards of pharmacy, and occupational health and safety organizations. These regulations often provide specific requirements for storing, labeling, and tracking medications and other controlled substances. Maintaining detailed records of your inventory, including lot numbers and expiration dates, is a key part of compliance.
Conclusion
Proper preservation and storage of mobile medical kits are ongoing responsibilities that require consistent attention, regular training, and a commitment to best practices. By understanding risks and implementing effective strategies, healthcare providers can ensure their kits are always ready to provide safe care.